Facebook Login Setup
Introduction
Section titled “Introduction”In this guide, you will learn how to setup Facebook Login with Capgo Social Login. You will need the following:
- A Facebook Developer Account
- Your app’s package name/bundle ID
- Access to a terminal for generating key hashes (Android)
General Setup
Section titled “General Setup”If you don’t already have a Facebook app created, follow these steps:
-
Create a Facebook App
Follow the tutorial to Create an App
-
Add Facebook Login to your app
In your Facebook Developer Dashboard, add the Facebook Login product to your app
-
Before you can release your app to the public, follow this tutorial to publish it
Important Information
Section titled “Important Information”Here’s where to find the key information you’ll need for integration:
-
CLIENT_TOKEN: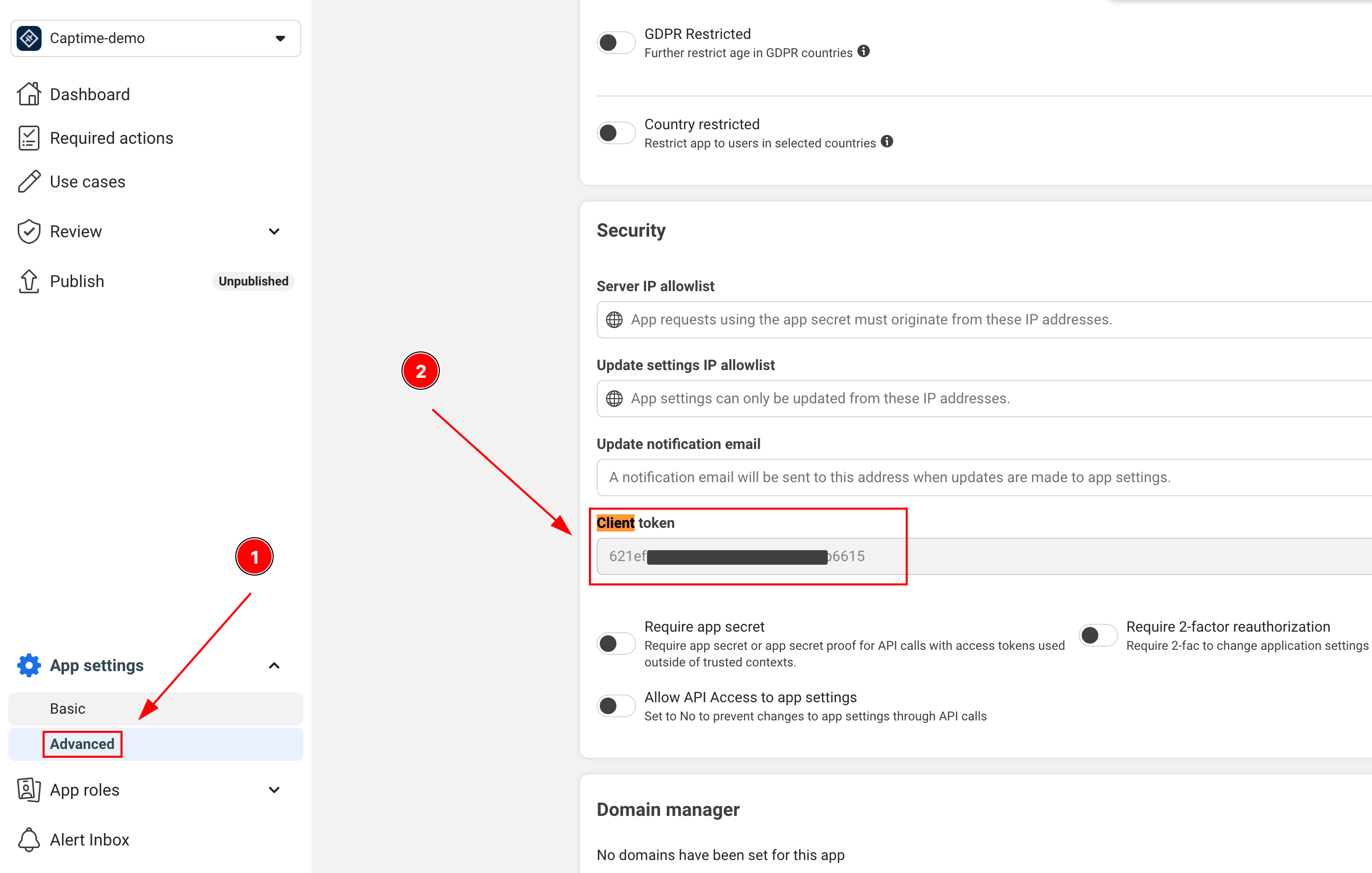
-
APP_ID: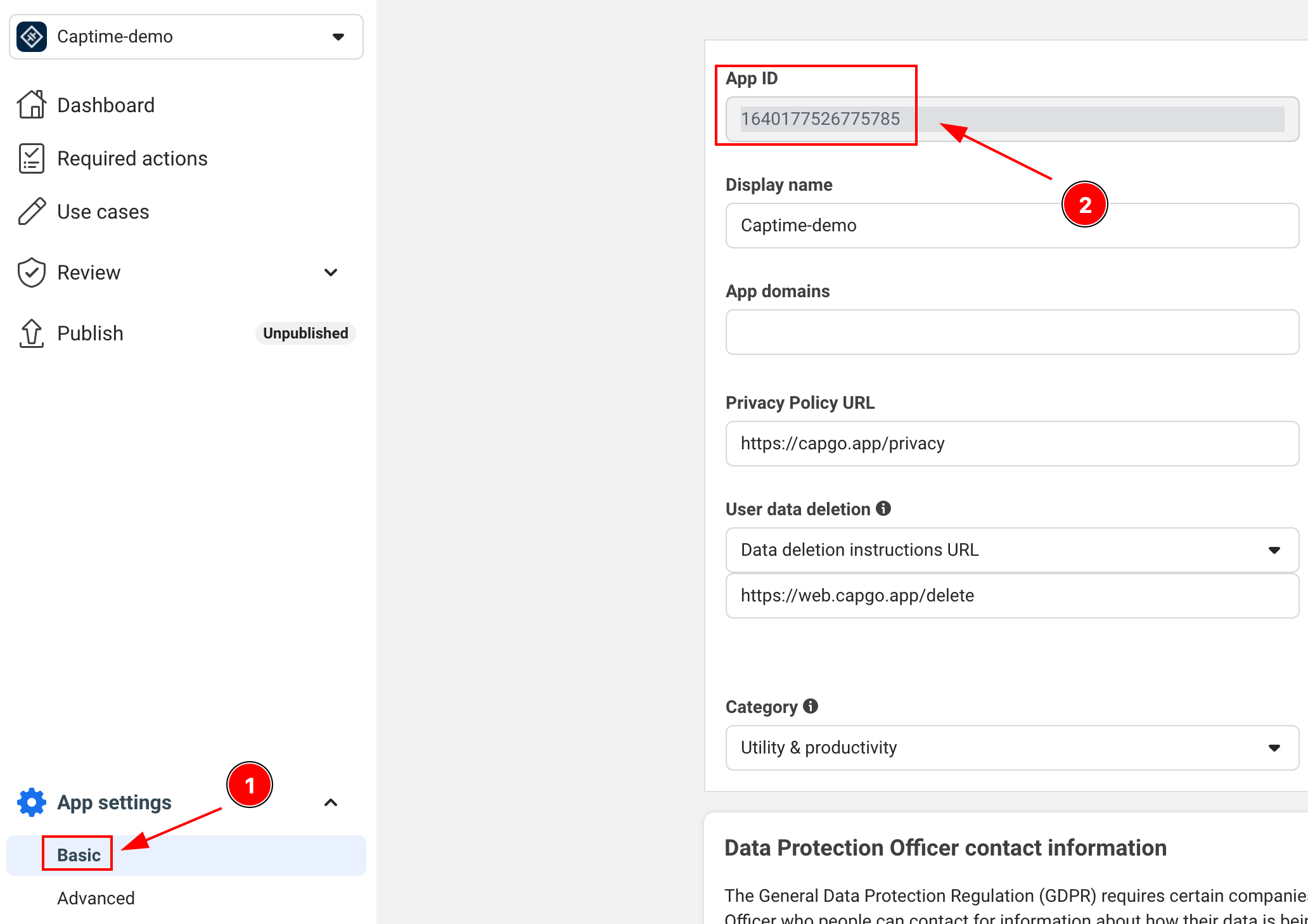
-
APP_NAME: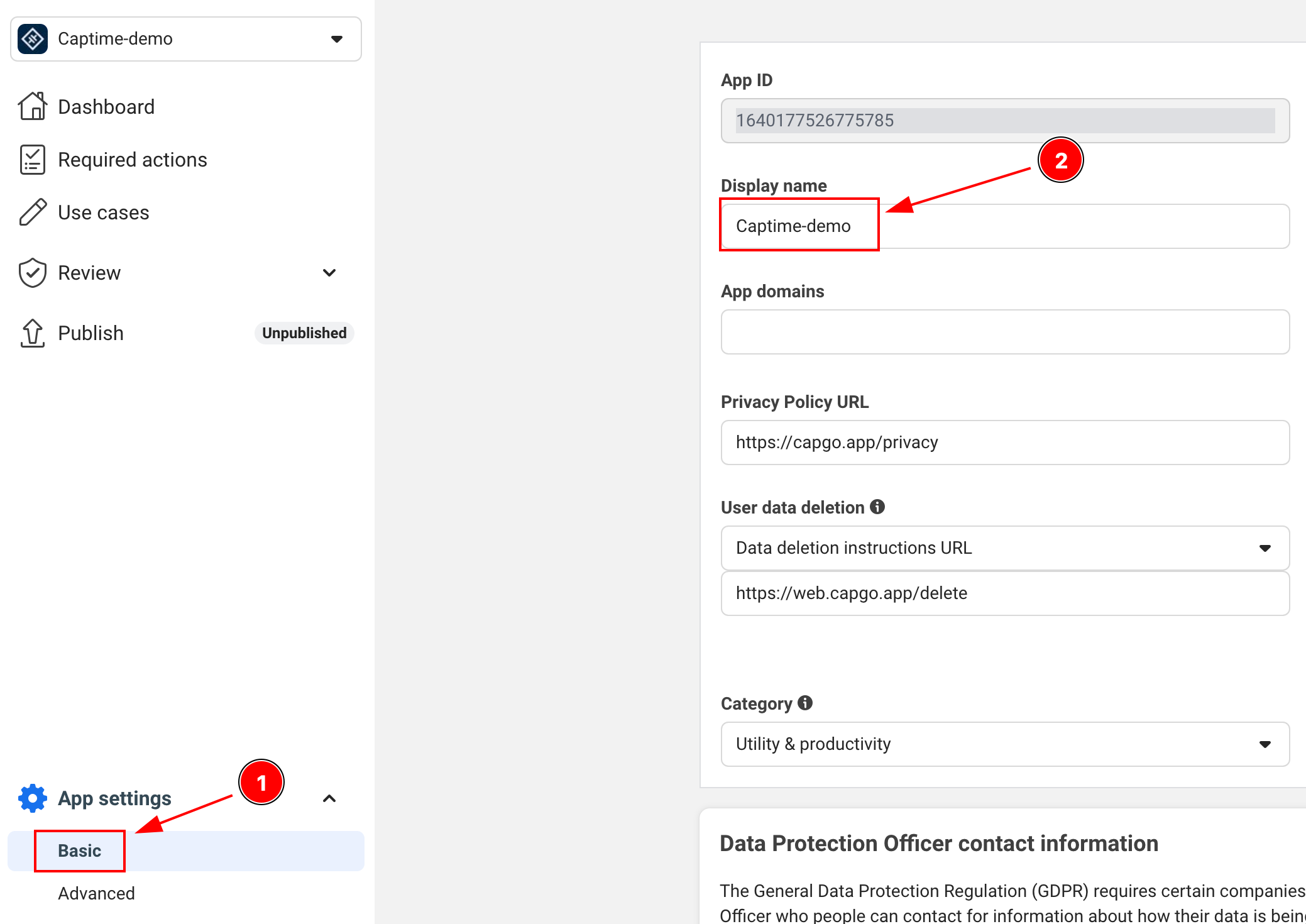
Android Setup
Section titled “Android Setup”-
Add internet permission to your
AndroidManifest.xmlEnsure this line is present:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/> -
Generate your Android key hash
This is a crucial security step required by Facebook. Open your terminal and run:
Terminal window keytool -exportcert -alias androiddebugkey -keystore ~/.android/debug.keystore | openssl sha1 -binary | openssl base64 -AWhen prompted for a password, use:
android -
Add the key hash to your Facebook app
- Go to your app’s dashboard on Facebook Developers
- Navigate to Settings > Basic
- Scroll down to “Android” section
- Click “Add Platform” if Android isn’t added yet and fill in the details
- Add the key hash you generated
- For production, add both debug and release key hashes
-
Update your
AndroidManifest.xmlto include:<application>...<activity android:name="com.facebook.FacebookActivity"android:configChanges="keyboard|keyboardHidden|screenLayout|screenSize|orientation"android:label="@string/app_name" /><activityandroid:name="com.facebook.CustomTabActivity"android:exported="true"><intent-filter><action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /><category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /><category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" /><data android:scheme="FB[APP_ID]" /></intent-filter></activity></application>
iOS Setup
Section titled “iOS Setup”-
Add the iOS platform in Facebook Developer Console
- Go to your app’s dashboard on Facebook Developers
- Navigate to Settings > Basic
- Scroll down to very bottom of the page and click “Add Platform”
- Select iOS and fill in the required details
-
Open your Xcode project and navigate to Info.plist
-
Add the following entries to your Info.plist:
<key>FacebookAppID</key><string>[APP-ID]</string><key>FacebookClientToken</key><string>[CLIENT-TOKEN]</string><key>FacebookDisplayName</key><string>[APP-NAME]</string><key>LSApplicationQueriesSchemes</key><array><string>fbapi</string><string>fb-messenger-share-api</string></array><key>CFBundleURLTypes</key><array><dict><key>CFBundleURLSchemes</key><array><string>fb[APP-ID]</string></array></dict></array> -
Modify the
AppDelegate.swiftimport FBSDKCoreKit@UIApplicationMainclass AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {// Override point for customization after application launch.// Initialize Facebook SDKFBSDKCoreKit.ApplicationDelegate.shared.application(application,didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: launchOptions)return true}func application(_ app: UIApplication, open url: URL, options: [UIApplication.OpenURLOptionsKey: Any] = [:]) -> Bool {// Called when the app was launched with a url. Feel free to add additional processing here,// but if you want the App API to support tracking app url opens, make sure to keep this callif (FBSDKCoreKit.ApplicationDelegate.shared.application(app,open: url,sourceApplication: options[UIApplication.OpenURLOptionsKey.sourceApplication] as? String,annotation: options[UIApplication.OpenURLOptionsKey.annotation])) {return true;} else {return ApplicationDelegateProxy.shared.application(app, open: url, options: options)}}}
Using Facebook Login in Your App
Section titled “Using Facebook Login in Your App”-
Initialize the Facebook login in your app
import { SocialLogin } from '@capgo/capacitor-social-login';// Initialize during app startupawait SocialLogin.initialize({facebook: {appId: 'APP_ID',clientToken: 'CLIENT_TOKEN',}}) -
Implement the login function
async function loginWithFacebook() {try {const result = await SocialLogin.login({provider: 'facebook',options: {permissions: ['email', 'public_profile'],limitedLogin: false // See Limited Login section below for important details}});console.log('Facebook login result:', result);// Handle successful login} catch (error) {console.error('Facebook login error:', error);// Handle error}} -
Get User Profile Data
After successful login, you can retrieve additional profile information:
async function getFacebookProfile() {try {const profileResponse = await SocialLogin.providerSpecificCall({call: 'facebook#getProfile',options: {fields: ['id', 'name', 'email', 'first_name', 'last_name', 'picture']}});console.log('Facebook profile:', profileResponse.profile);return profileResponse.profile;} catch (error) {console.error('Failed to get Facebook profile:', error);return null;}}// Example usage after loginasync function loginAndGetProfile() {const loginResult = await loginWithFacebook();if (loginResult) {const profile = await getFacebookProfile();if (profile) {console.log('User ID:', profile.id);console.log('Name:', profile.name);console.log('Email:', profile.email);console.log('Profile Picture:', profile.picture?.data?.url);}}}Token Type Limitation: The
getProfilecall only works when you have an access token (standard login with tracking allowed). If the user denied tracking or you’re using limited login (JWT token only), this call will fail. In that case, use the profile data provided in the initial login response.
⚠️ Critical: Backend Token Handling
Section titled “⚠️ Critical: Backend Token Handling”Your backend must handle two different token types because iOS users can receive either access tokens or JWT tokens depending on their App Tracking Transparency choice, while Android users always receive access tokens.
Token Types by Platform
Section titled “Token Types by Platform”| Platform | limitedLogin Setting | User ATT Choice | Result Token Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| iOS | true | Any | JWT Token |
| iOS | false | Allows tracking | Access Token |
| iOS | false | Denies tracking | JWT Token (auto-override) |
| Android | Any | N/A | Access Token (always) |
Backend Implementation
Section titled “Backend Implementation”-
Detect Token Type and Handle Accordingly
async function loginWithFacebook() {try {const loginResult = await SocialLogin.login({provider: 'facebook',options: {permissions: ['email', 'public_profile'],limitedLogin: false // iOS: depends on ATT, Android: ignored}});if (loginResult.accessToken) {// Access token (Android always, iOS when tracking allowed)return handleAccessToken(loginResult.accessToken.token);} else if (loginResult.idToken) {// JWT token (iOS only when tracking denied or limitedLogin: true)return handleJWTToken(loginResult.idToken);}} catch (error) {console.error('Facebook login error:', error);}} -
Firebase Integration Example
import { OAuthProvider, FacebookAuthProvider, signInWithCredential } from 'firebase/auth';async function handleAccessToken(accessToken: string, nonce: string) {// For access tokens, use OAuthProvider (new method)const fbOAuth = new OAuthProvider("facebook.com");const credential = fbOAuth.credential({idToken: accessToken,rawNonce: nonce});try {const userResponse = await signInWithCredential(auth, credential);return userResponse;} catch (error) {console.error('Firebase OAuth error:', error);return false;}}async function handleJWTToken(jwtToken: string) {// For JWT tokens, send to your backend for validationtry {const response = await fetch('/api/auth/facebook-jwt', {method: 'POST',headers: {'Content-Type': 'application/json',},body: JSON.stringify({ jwtToken })});const result = await response.json();return result;} catch (error) {console.error('JWT validation error:', error);return false;}} -
Backend JWT Validation
// Backend: Validate JWT token from Facebookimport jwt from 'jsonwebtoken';import { Request, Response } from 'express';app.post('/api/auth/facebook-jwt', async (req: Request, res: Response) => {const { jwtToken } = req.body;try {// Verify JWT token with Facebook's public key// See: https://developers.facebook.com/docs/facebook-login/limited-login/token/validating/#standard-claimsconst decoded = jwt.verify(jwtToken, getFacebookPublicKey(), {algorithms: ['RS256'],audience: process.env.FACEBOOK_APP_ID,issuer: 'https://www.facebook.com' // From: https://www.facebook.com/.well-known/openid-configuration/?_rdr});// Extract user info from JWTconst userInfo = {id: decoded.sub,email: decoded.email,name: decoded.name,isJWTAuth: true};// Create your app's session/tokenconst sessionToken = createUserSession(userInfo);res.json({success: true,token: sessionToken,user: userInfo});} catch (error) {console.error('JWT validation failed:', error);res.status(401).json({ success: false, error: 'Invalid token' });}}); -
Generic Backend Token Handler
// Handle both token types in your backendasync function authenticateFacebookUser(tokenData: any) {if (tokenData.accessToken) {// Handle access token - validate with Facebook Graph APIconst response = await fetch(`https://graph.facebook.com/me?access_token=${tokenData.accessToken}&fields=id,name,email`);const userInfo = await response.json();return {user: userInfo,tokenType: 'access_token',expiresIn: tokenData.expiresIn || 3600};} else if (tokenData.jwtToken) {// Handle JWT token - decode and validate// See: https://developers.facebook.com/docs/facebook-login/limited-login/token/validating/#standard-claimsconst decoded = jwt.verify(tokenData.jwtToken, getFacebookPublicKey());return {user: {id: decoded.sub,name: decoded.name,email: decoded.email},tokenType: 'jwt',expiresIn: decoded.exp - Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000)};} else {throw new Error('No valid token provided');}}
Key Considerations
Section titled “Key Considerations”Access Token (Standard Login):
- ✅ Android: Always available (iOS-only restrictions don’t apply)
- ✅ iOS: Only when user explicitly allows app tracking
- ✅ Can be used to access Facebook Graph API
- ✅ Longer expiration times
- ✅ More user data available
- ❌ Becoming less common on iOS as users increasingly deny tracking
JWT Token (iOS-Only Privacy Mode):
- ❌ Android: Never occurs (not supported)
- ✅ iOS: When tracking denied or
limitedLogin: true - ✅ Respects iOS user privacy preferences
- ❌ Contains basic user info only
- ❌ Shorter expiration times
- ❌ No access to Facebook Graph API
- ⚠️ Now the most common scenario for iOS users
Platform-Specific Behavior:
- iOS apps: Must handle both access tokens AND JWT tokens
- Android apps: Only need to handle access tokens
- Cross-platform apps: Must implement both token handling methods
Secure Context Requirements (Web/Capacitor)
Section titled “Secure Context Requirements (Web/Capacitor)”Crypto API Limitations
Section titled “Crypto API Limitations”The updated Facebook login flow requires the Web Crypto API for nonce generation, which is only available in secure contexts:
// This requires secure context (HTTPS or localhost)async function sha256(message: string) { const msgBuffer = new TextEncoder().encode(message); const hashBuffer = await crypto.subtle.digest("SHA-256", msgBuffer); // ❌ Fails in insecure context // ...}Development Environment Issues
Section titled “Development Environment Issues”Common Problem: ionic serve with HTTP URLs breaks Facebook authentication
| Environment | Crypto API Available | Facebook Login Works |
|---|---|---|
http://localhost:3000 | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
http://127.0.0.1:3000 | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
http://192.168.1.100:3000 | ❌ No | ❌ No |
https://any-domain.com | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
Solutions for Capacitor Development
Section titled “Solutions for Capacitor Development”-
Use localhost for web testing
Terminal window # Instead of ionic serve --host=0.0.0.0ionic serve --host=localhost -
Enable HTTPS in Ionic
Terminal window ionic serve --ssl -
Test on actual devices
Terminal window # Capacitor apps run in secure context on devicesionic cap run iosionic cap run android -
Alternative nonce generation for development
async function generateNonce() {if (typeof crypto !== 'undefined' && crypto.subtle) {// Secure context - use crypto.subtlereturn await sha256(Math.random().toString(36).substring(2, 10));} else {// Fallback for development (not secure for production)console.warn('Using fallback nonce - not secure for production');return btoa(Math.random().toString(36).substring(2, 10));}}
Firebase Integration Note
Section titled “Firebase Integration Note”Recent Firebase documentation requires JWT tokens with nonces for Facebook authentication, regardless of login settings. This approach works with both limitedLogin: true and limitedLogin: false:
// Both modes can return JWT tokens depending on user choice const loginResult = await SocialLogin.login({ provider: 'facebook', options: { permissions: ['email', 'public_profile'], limitedLogin: false, // true = always JWT, false = depends on user tracking choice nonce: nonce } });Development Limitation: If you’re using ionic serve on a network IP (not localhost), Facebook login will fail due to crypto API restrictions. Use localhost or HTTPS for web testing.
Troubleshooting
Section titled “Troubleshooting”Common Issues and Solutions
Section titled “Common Issues and Solutions”-
Key hash errors on Android
- Double check that you’ve added the correct key hash to the Facebook dashboard
- For release builds, make sure you’ve added both debug and release key hashes
- Verify you’re using the correct keystore when generating the hash
-
Facebook login button doesn’t appear
- Verify all manifest entries are correct
- Check that your Facebook App ID and Client Token are correct
- Ensure you’ve properly initialized the SDK
-
Common iOS issues
- Make sure all Info.plist entries are correct
- Verify URL schemes are properly configured
- Check that your bundle ID matches what’s registered in the Facebook dashboard
Testing
Section titled “Testing”-
Before testing, add test users in the Facebook Developer Console
- Go to Roles > Test Users
- Create a test user
- Use these credentials for testing
-
Test both debug and release builds
- Debug build with debug key hash
- Release build with release key hash
- Test on both emulator and physical devices
Remember to test the full login flow, including:
- Successful login
- Login cancellation
- Error handling
- Logout functionality
