암호화
Capgo는 앱 번들에 대한 강력한 엔드투엔드 암호화를 제공하여 JavaScript 코드와 자산이 전송 및 저장 중에 보호되도록 합니다. 이 암호화 시스템은 라이브 업데이트의 편의성을 유지하면서 앱의 보안을 완전히 제어할 수 있도록 설계되었습니다.
Capgo의 암호화 시스템은 업계 표준 암호화 방법을 사용하여 번들을 무단 액세스로부터 보호합니다. 암호화가 활성화되면 번들은 개발 환경을 떠나기 전에 암호화되며 사용자의 기기에서 앱에 의해 복호화될 때까지 암호화된 상태로 유지됩니다.
진정한 엔드투엔드 암호화: 업데이트에 서명만 하는(코드를 공개적으로 읽을 수 있도록 남겨두는) 다른 OTA 업데이트 플랫폼과 달리 Capgo는 진정한 엔드투엔드 암호화를 제공합니다. 즉, 사용자만 업데이트를 복호화할 수 있으며 Capgo 자체를 포함한 다른 누구도 할 수 없습니다. 번들 콘텐츠는 전체 전송 프로세스 동안 완전히 비공개이며 읽을 수 없습니다.
암호화 작동 방식
Section titled “암호화 작동 방식”Capgo는 최적의 보안과 성능을 위해 RSA와 AES 암호화를 결합한 하이브리드 암호화 접근 방식을 사용합니다:
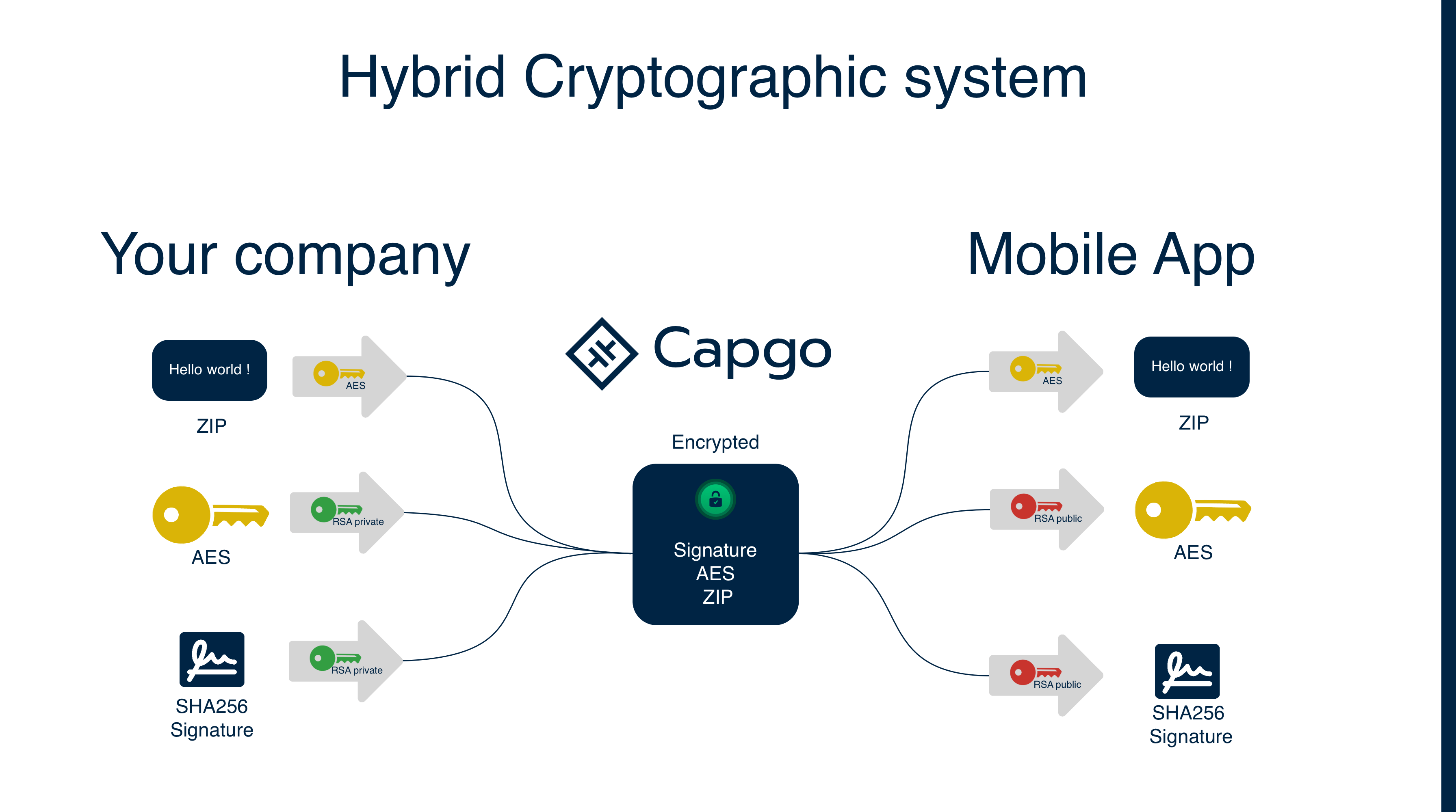
1. 키 생성
Section titled “1. 키 생성”- 개인 키: 개발 환경에서 생성되고 안전하게 저장됨(암호화에 사용)
- 공개 키: 개인 키에서 파생되어 앱의 Capacitor 구성에 저장됨(복호화에 사용)
- 세션 키: 각 번들 업로드에 대해 생성되는 무작위 AES 키
2. 암호화 프로세스
Section titled “2. 암호화 프로세스”- 각 번들 업로드에 대해 무작위 AES 세션 키가 생성됩니다
- 번들이 AES 세션 키를 사용하여 암호화됩니다
- 번들 체크섬이 계산됩니다
- AES 세션 키와 체크섬이 함께 RSA 개인 키를 사용하여 암호화됩니다(“서명” 생성)
- 암호화된 번들과 암호화된 서명이 저장됩니다
체크섬은 변조를 방지하기 위해 AES 키와 함께 암호화됩니다. RSA 개인 키만 이 서명을 생성할 수 있고 해당 공개 키만 복호화할 수 있으므로 AES 세션 키와 예상 체크섬이 진품이며 공격자에 의해 수정되지 않았음을 보장합니다.
3. 복호화 프로세스
Section titled “3. 복호화 프로세스”- 앱이 암호화된 번들과 암호화된 서명을 다운로드합니다
- Capgo SDK는 RSA 공개 키(앱에 저장됨)를 사용하여 서명을 복호화합니다
- 이를 통해 AES 세션 키와 원래 체크섬이 드러납니다
- AES 세션 키를 사용하여 번들을 복호화합니다
- 복호화된 번들의 체크섬이 계산되고 무결성 확인을 위해 원래 체크섬과 비교됩니다
이 프로세스는 공격자가 암호화된 번들을 가로채더라도 AES 세션 키를 수정하거나 가짜 체크섬을 제공할 수 없도록 보장합니다. 왜냐하면 공개 키가 복호화할 수 있는 유효한 서명을 생성하려면 개인 키가 필요하기 때문입니다.
Capgo vs 다른 플랫폼
Section titled “Capgo vs 다른 플랫폼”| 기능 | Capgo | 다른 OTA 플랫폼 |
|---|---|---|
| 번들 콘텐츠 | 완전히 암호화(읽을 수 없음) | 공개적으로 읽을 수 있음 |
| 보안 방법 | 진정한 엔드투엔드 암호화 | 코드 서명만 |
| 개인정보 보호 수준 | 제로 지식(Capgo도 코드를 읽을 수 없음) | 플랫폼이 코드에 액세스 가능 |
| 보호 | 콘텐츠 + 무결성 + 진위성 | 무결성 + 진위성만 |
이것이 중요한 이유:
- 코드 서명은 업데이트가 변조되지 않았고 올바른 출처에서 왔음을 확인할 뿐입니다
- 엔드투엔드 암호화는 실제 코드 콘텐츠가 전송 및 저장 중에 비공개이고 읽을 수 없도록 보장합니다
- Capgo의 진정한 엔드투엔드 암호화를 사용하면 사용자만 업데이트를 복호화할 수 있으며 Capgo 자체를 포함한 다른 누구도 할 수 없습니다
암호화 방법
Section titled “암호화 방법”Capgo는 Encryption V2를 표준 암호화 방법으로 사용합니다:
Encryption V2(현재 표준)
Section titled “Encryption V2(현재 표준)”- 향상된 보안을 위해 RSA-4096 사용
- 인증된 암호화를 위한 AES-256-GCM
- 무결성 확인 제공
- 더 나은 성능과 보안
Encryption V1(더 이상 사용되지 않음)
Section titled “Encryption V1(더 이상 사용되지 않음)”- 키 암호화에 RSA-2048 사용
- 번들 암호화에 AES-256-CBC 사용
- 현재 CLI에서 더 이상 사용 불가
- V1을 사용하는 레거시 앱은 V2로 마이그레이션해야 함
암호화 설정
Section titled “암호화 설정”1단계: 암호화 키 생성
Section titled “1단계: 암호화 키 생성”먼저 Capgo CLI를 사용하여 암호화 키를 생성합니다:
# 새 암호화 키 생성(현재 디렉토리에 파일 생성)npx @capgo/cli@latest key create다음이 생성됩니다:
.capgo_key_v2: 개인 키(안전하게 보관하세요!).capgo_key_v2.pub: 공개 키(앱에서 사용)
이 파일들은 명령을 실행하는 현재 디렉토리에 생성됩니다.
2단계: Capacitor 구성에 공개 키 저장(필수)
Section titled “2단계: Capacitor 구성에 공개 키 저장(필수)”모바일 앱이 번들을 복호화할 수 있도록 Capacitor 구성에 공개 키를 저장해야 합니다:
# 파일에서 Capacitor 구성으로 공개 키 저장(필수)npx @capgo/cli@latest key save --key ./.capgo_key_v2.pub
# 또는 공개 키 데이터를 직접 저장npx @capgo/cli@latest key save --key-data "$CAPGO_PUBLIC_KEY"3단계: Capacitor 플랫폼 동기화(필수)
Section titled “3단계: Capacitor 플랫폼 동기화(필수)”공개 키를 저장한 후 업데이트된 구성을 네이티브 레이어로 복사하기 위해 Capacitor 플랫폼을 동기화해야 합니다:
# 구성을 네이티브로 복사하기 위해 플랫폼 동기화npx cap sync번들 암호화
Section titled “번들 암호화”방법 1: 업로드 중 암호화
Section titled “방법 1: 업로드 중 암호화”가장 간단한 방법은 업로드 프로세스 중에 암호화하는 것입니다:
# 자동 암호화로 업로드npx @capgo/cli@latest bundle upload --key-v2
# 외부 스토리지의 경우 먼저 암호화해야 합니다(아래 수동 암호화 워크플로우 참조)방법 2: 수동 암호화 워크플로우
Section titled “방법 2: 수동 암호화 워크플로우”더 많은 제어를 위해 번들을 수동으로 암호화할 수 있습니다:
-
zip 번들 생성:
Terminal window npx @capgo/cli@latest bundle zip com.example.app --path ./dist --key-v2 -
번들 암호화:
Terminal window npx @capgo/cli@latest bundle encrypt ./com.example.app.zip CHECKSUM_FROM_STEP_1 -
스토리지에 업로드(예: S3)하고 Capgo에 등록:
Terminal window # 먼저 암호화된 번들을 스토리지에 업로드(예: AWS S3)aws s3 cp ./encrypted-bundle.zip s3://your-bucket/encrypted-bundle.zip# 그런 다음 외부 URL을 사용하여 Capgo에 등록npx @capgo/cli@latest bundle upload --external https://your-storage.com/encrypted-bundle.zip --iv-session-key IV_SESSION_KEY_FROM_STEP_2
키를 안전하게 저장
Section titled “키를 안전하게 저장”개인 키 옵션:
-
파일 기반(로컬 개발):
Terminal window # 프로젝트 루트의 .capgo_key_v2 파일로 저장된 키npx @capgo/cli@latest bundle upload --key-v2 -
환경 변수(CI/CD):
Terminal window # CI용 환경 변수에 저장export CAPGO_PRIVATE_KEY="$(cat .capgo_key_v2)"npx @capgo/cli@latest bundle upload --key-data-v2 "$CAPGO_PRIVATE_KEY"
공개 키 설정(필수):
# 모바일 앱을 위해 Capacitor 구성에 공개 키를 저장해야 함npx @capgo/cli@latest key save --key ./.capgo_key_v2.pub프로덕션 환경:
- 안전한 키 관리 서비스에 개인 키 저장(AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault 등)
- 개인 키에 CI/CD 비밀 관리 사용
- 절대 개인 키를 버전 관리에 커밋하지 마세요
키 사용:
- 개인 키: 번들 업로드 중 암호화를 위해 CLI에서 사용(안전하게 보관)
- 공개 키: 기기에서 복호화를 위해 앱 구성에 저장(커밋해도 안전)
보안 강화를 위해 암호화 키를 정기적으로 교체하세요:
-
새 키 생성:
Terminal window # 먼저 원하는 디렉토리로 이동한 다음 키 생성mkdir ./new-keys && cd ./new-keysnpx @capgo/cli@latest key create -
Capacitor 구성에 새 공개 키 저장:
Terminal window npx @capgo/cli@latest key save --key ./new-keys/.capgo_key_v2.pub -
앱 구성 업데이트 새 공개 키로
-
새 키로 암호화된 번들을 업로드하기 전에 업데이트된 앱 배포
보안 모범 사례
Section titled “보안 모범 사례”- 개인 키를 절대 공유하지 마세요 환경이나 팀원 간에
- 다른 키를 사용하세요 다른 환경별로(개발, 스테이징, 프로덕션)
- 키를 정기적으로 교체하세요(권장: 6-12개월마다)
- 키를 안전하게 저장하세요 적절한 키 관리 시스템 사용
- 항상 확인하세요 복호화 후 번들 무결성
- 모니터링하세요 비정상적인 다운로드 패턴이나 실패
- HTTPS를 사용하세요 모든 번들 URL에(모바일 앱 필수)
- 구현하세요 복호화 실패에 대한 적절한 오류 처리
액세스 제어
Section titled “액세스 제어”- 액세스를 제한하세요 승인된 직원에게만 암호화 키
- 역할 기반 액세스를 사용하세요 키 관리 작업에
- 감사하세요 키 사용 및 액세스를 정기적으로
- 구현하세요 적절한 백업 및 복구 절차
암호화 문제 해결
Section titled “암호화 문제 해결”일반적인 문제
Section titled “일반적인 문제”복호화 실패:
- 개인 키가 암호화에 사용된 공개 키와 일치하는지 확인
ivSessionKey가 올바른지 확인- Encryption V2를 사용 중인지 확인(V1은 더 이상 지원되지 않음)
키 관련 오류:
- 개인 키 형식이 올바른지 확인(PEM 형식)
- 저장/전송 중 키가 손상되지 않았는지 확인
- 앱 구성에서 키에 적절한 권한이 있는지 확인
성능 문제:
- 대용량 번들은 암호화/복호화에 시간이 더 걸릴 수 있습니다
- 번들 크기를 줄이기 위해 차등 업데이트 사용 고려
- 복호화 중 기기 성능 모니터링
디버그 명령
Section titled “디버그 명령”암호화 상태 확인:
npx @capgo/cli@latest app debug암호화/복호화 워크플로우 테스트:
# 전체 워크플로우 테스트: zip → encrypt → decrypt → unzipnpx @capgo/cli@latest bundle zip com.example.app --key-v2npx @capgo/cli@latest bundle encrypt ./com.example.app.zip CHECKSUM --jsonnpx @capgo/cli@latest bundle decrypt ./encrypted-bundle.zip IV_SESSION_KEY규정 준수 및 표준
Section titled “규정 준수 및 표준”Capgo의 암호화 구현은 업계 표준을 따릅니다:
- AES-256: FIPS 140-2 승인 암호화 알고리즘
- RSA-4096: 키 보호를 위한 강력한 비대칭 암호화
- GCM 모드: 기밀성과 진위성 모두 제공
- 보안 랜덤: 암호학적으로 안전한 난수 생성
이를 통해 Capgo는 다음을 준수해야 하는 애플리케이션에 적합합니다:
- GDPR(일반 데이터 보호 규정)
- HIPAA(건강 보험 양도 및 책임에 관한 법률)
- SOC 2(서비스 조직 제어 2)
- ISO 27001(정보 보안 관리)
성능 고려 사항
Section titled “성능 고려 사항”암호화 오버헤드
Section titled “암호화 오버헤드”- 번들 크기: 암호화된 번들은 약간 더 큽니다(~1-2% 오버헤드)
- 처리 시간: 암호화/복호화는 최소한의 지연 시간을 추가합니다
- 메모리 사용량: 암호화/복호화 작업 중 일시적으로 증가
- 암호화된 데이터 전송을 최소화하기 위해 차등 업데이트 사용
- 이미지를 WebP 형식으로 변환하여 번들 크기 최적화
- 번들링하기 전에 JavaScript 및 CSS 파일 최소화
- 사용하지 않는 종속성 및 코드 제거
- 오래되거나 느린 기기에서 기기 성능 모니터링
- 자체 인프라와 함께 암호화를 사용하려면 Custom Storage에 대해 알아보기
- 환경 전반에 걸쳐 암호화된 번들을 관리하려면 Channels 살펴보기
- 암호화된 배포를 자동화하려면 CI/CD Integration 설정
