API Keys
Ce contenu n'est pas encore disponible dans votre langue.
API keys are used to authenticate requests to the Capgo API. Each key can have different permissions (modes) to control access levels. Keys are organization-specific and should be managed carefully as they grant access to your Capgo resources.
Key Modes
Section titled “Key Modes”- read: Can only read data, no modifications allowed
- upload: Can read, modify, and upload new bundles
- write: Can read, modify data, and upload bundles
- all: Full access to all operations
Key modes follow a stepped/gradual schema. If you have an upload key, and then you create a write key, the write key will be able to do everything that the upload key could. Please take a look at the following diagram to better understand how API keys work.
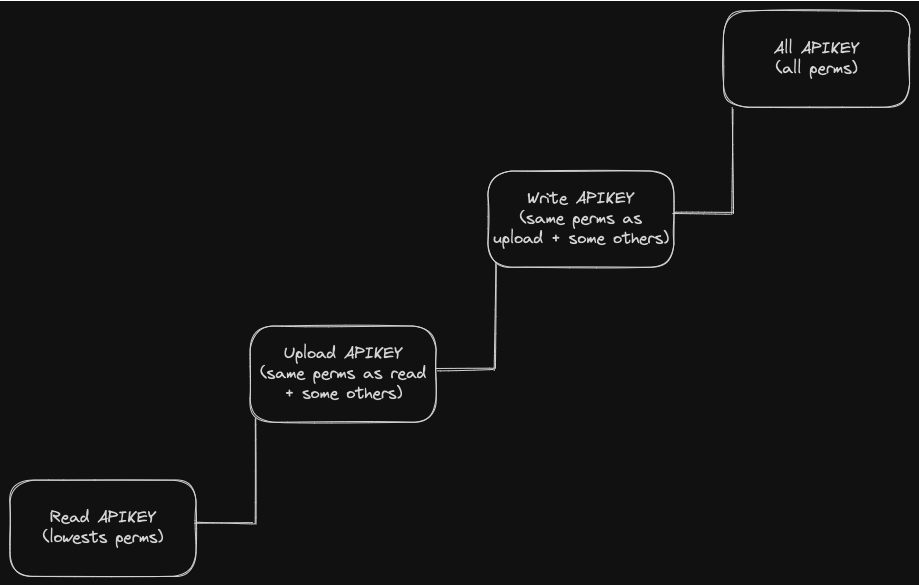
Subkeys with Limited Rights
Section titled “Subkeys with Limited Rights”You can create subkeys with limited access to specific apps or organizations. This is useful for restricting access to certain resources while still allowing operations on others. Use the limited_to_apps and limited_to_orgs parameters when creating a key to define these restrictions.
Encrypted Keys
Section titled “Encrypted Keys”You can create encrypted (hashed) API keys for enhanced security. When creating an encrypted key:
- The key is hashed using SHA-256 before being stored in the database
- The plain key is returned only once in the creation response - save it immediately
- The key cannot be retrieved or viewed again after creation
- If you lose an encrypted key, you must create a new one
Use the hashed: true parameter when creating a key to enable encryption. This is the recommended approach for production environments.
Key Expiration
Section titled “Key Expiration”API keys can have an expiration date to limit the window of exposure if a key is compromised. When an expiration date is set:
- The key stops working after the specified date and time
- Requests using expired keys will be rejected with an error
- Expired keys are automatically cleaned up after 30 days
Organizations can enforce expiration policies:
- Require expiration: All API keys must have an expiration date
- Maximum expiration period: Limit how far in the future an expiration date can be set
Security Best Practices
Section titled “Security Best Practices”- Principle of Least Privilege: Always use the most restrictive mode that still allows your integration to function
- Use Encrypted Keys: Create hashed keys for production to protect against database breaches
- Set Expiration Dates: Use expiration dates to limit the lifetime of your keys
- Regular Rotation: Rotate your API keys periodically
- Secure Storage: Store API keys securely and never commit them to version control
- Monitoring: Monitor API key usage and revoke any compromised keys immediately
- Limited Subkeys: Use subkeys with limited rights for specific integrations to minimize risk
Endpoints
Section titled “Endpoints”https://api.capgo.app/apikey/
Retrieve all API keys associated with your account.
Response Type
Section titled “Response Type”interface ApiKey { created_at: string | null id: number key: string | null // null for encrypted keys mode: 'read' | 'write' | 'upload' | 'all' name: string updated_at: string | null user_id: string limited_to_apps?: string[] limited_to_orgs?: string[] expires_at?: string | null // ISO 8601 date, null means never expires}Note: For encrypted keys, the
keyfield will benullin GET responses since the plain key is only shown once during creation.
Example Request
Section titled “Example Request”curl -H "authorization: your-api-key" https://api.capgo.app/apikey/Example Response
Section titled “Example Response”{ "data": [ { "id": 1, "key": "ak_123...", "mode": "read", "name": "CI/CD Read Key", "created_at": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z", "updated_at": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z", "user_id": "user_123" }, { "id": 2, "key": "ak_456...", "mode": "upload", "name": "Deploy Bot", "created_at": "2024-01-02T00:00:00Z", "updated_at": "2024-01-02T00:00:00Z", "user_id": "user_123", "limited_to_apps": ["com.demo.app"] } ]}https://api.capgo.app/apikey/
Create a new API key for a specific organization.
Request Body
Section titled “Request Body”interface ApiKeyCreate { name: string mode: 'read' | 'write' | 'upload' | 'all' limited_to_apps?: string[] limited_to_orgs?: string[] hashed?: boolean // Create an encrypted key (recommended for production) expires_at?: string // ISO 8601 date for key expiration}Example Request (Standard Key)
Section titled “Example Request (Standard Key)”curl -X POST \ -H "authorization: your-api-key" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "name": "Limited Read Key", "mode": "read", "limited_to_apps": ["com.demo.app"] }' \ https://api.capgo.app/apikey/Example Request (Encrypted Key with Expiration)
Section titled “Example Request (Encrypted Key with Expiration)”curl -X POST \ -H "authorization: your-api-key" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "name": "Secure CI Key", "mode": "upload", "hashed": true, "expires_at": "2025-06-01T00:00:00Z" }' \ https://api.capgo.app/apikey/Example Response (Standard Key)
Section titled “Example Response (Standard Key)”{ "apikey": { "id": 3, "key": "ak_789...", "mode": "read", "name": "Limited Read Key", "created_at": "2024-02-12T00:00:00Z", "user_id": "user_123", "limited_to_apps": ["com.demo.app"] }}Example Response (Encrypted Key)
Section titled “Example Response (Encrypted Key)”{ "apikey": { "id": 4, "key": "ak_abc123...", "mode": "upload", "name": "Secure CI Key", "created_at": "2024-02-12T00:00:00Z", "user_id": "user_123", "expires_at": "2025-06-01T00:00:00Z" }}Important: For encrypted keys, the
keyvalue in this response is the only time you will see the plain key. Save it immediately in a secure location. Subsequent GET requests will returnnullfor thekeyfield.
DELETE
Section titled “DELETE”https://api.capgo.app/apikey/:id/
Delete an existing API key. Use this to revoke access immediately.
Parameters
Section titled “Parameters”id: The ID of the API key to delete (numeric identifier, not the key string itself)
Example Request
Section titled “Example Request”curl -X DELETE -H "authorization: your-api-key" https://api.capgo.app/apikey/1/Success Response
Section titled “Success Response”{ "success": true}Common Use Cases
Section titled “Common Use Cases”- CI/CD Integration: Create read-only keys for CI pipelines to check deployment status
- Deployment Automation: Use upload mode keys for automated deployment scripts
- Monitoring Tools: Use read mode keys for external monitoring integrations
- Admin Access: Use all mode keys sparingly for administrative tools
- Limited Access: Create subkeys with limited rights to specific apps or organizations for third-party integrations
Error Handling
Section titled “Error Handling”Common error scenarios and their responses:
// Invalid mode{ "error": "Invalid mode specified. Must be one of: read, write, upload, all", "status": "KO"}
// Key not found{ "error": "API key not found", "status": "KO"}
// Permission denied{ "error": "Insufficient permissions to manage API keys", "status": "KO"}
// Expired API key used for authentication{ "error": "API key has expired", "status": "KO"}
// Invalid expiration date (in the past){ "error": "Expiration date must be in the future", "status": "KO"}
// Organization requires expiration{ "error": "Organization policy requires an expiration date for API keys", "status": "KO"}
// Expiration exceeds organization limit{ "error": "Expiration date exceeds organization maximum of 90 days", "status": "KO"}