Facebookログインの設定
このガイドでは、Capgo Social LoginでFacebookログインを設定する方法を学びます。次のものが必要です:
- Facebook Developer Account
- アプリのpackage name/bundle ID
- key hashを生成するためのターミナルへのアクセス(Android)
一般的な設定
Section titled “一般的な設定”まだFacebookアプリを作成していない場合は、次の手順に従ってください:
-
Facebookアプリを作成する
Create an Appのチュートリアルに従ってください
-
アプリにFacebookログインを追加する
Facebook Developer Dashboardで、アプリにFacebook Loginプロダクトを追加します
-
アプリを一般公開する前に、このチュートリアルに従って公開してください
統合に必要な重要な情報の場所は次のとおりです:
-
CLIENT_TOKEN: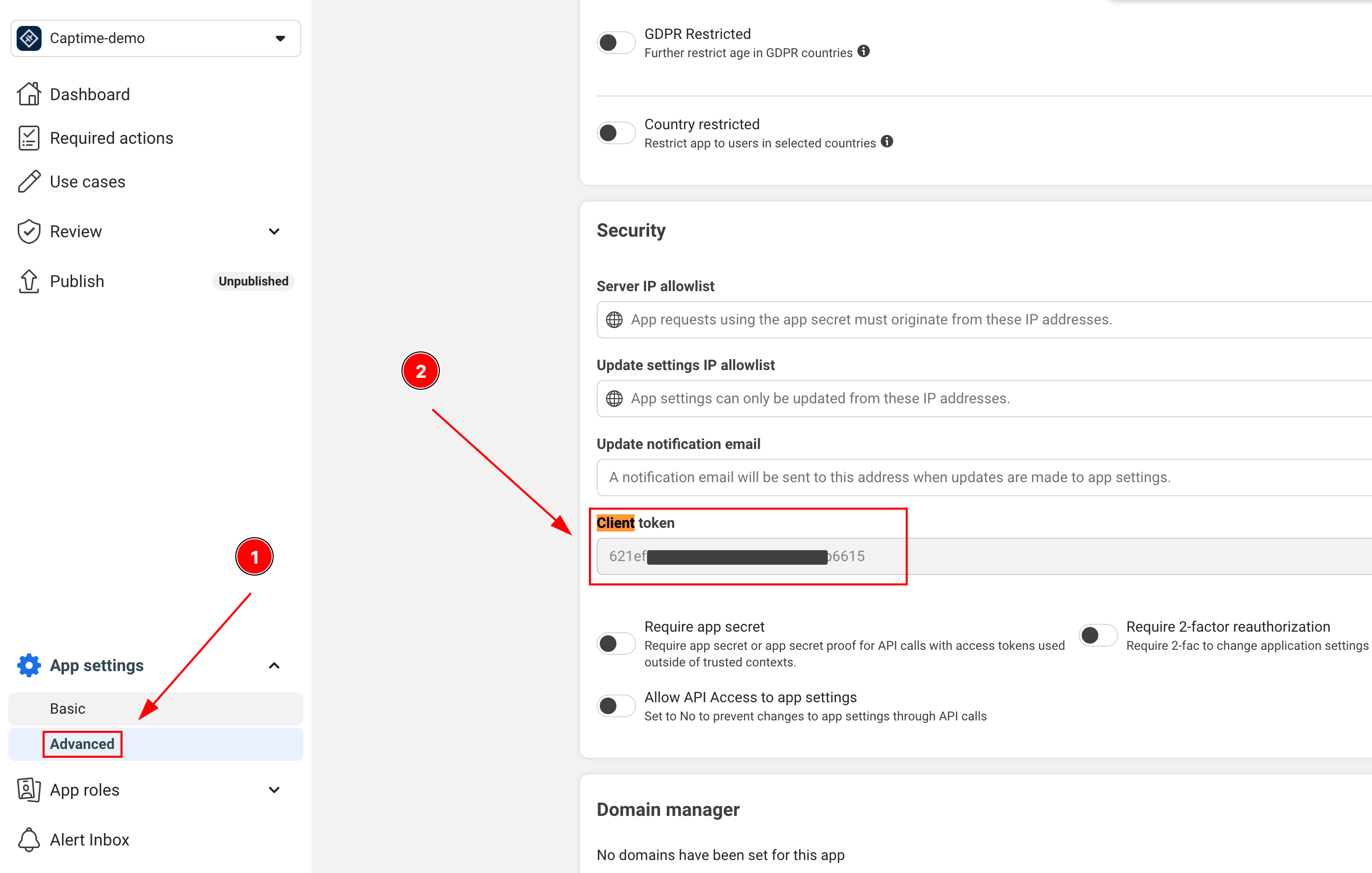
-
APP_ID: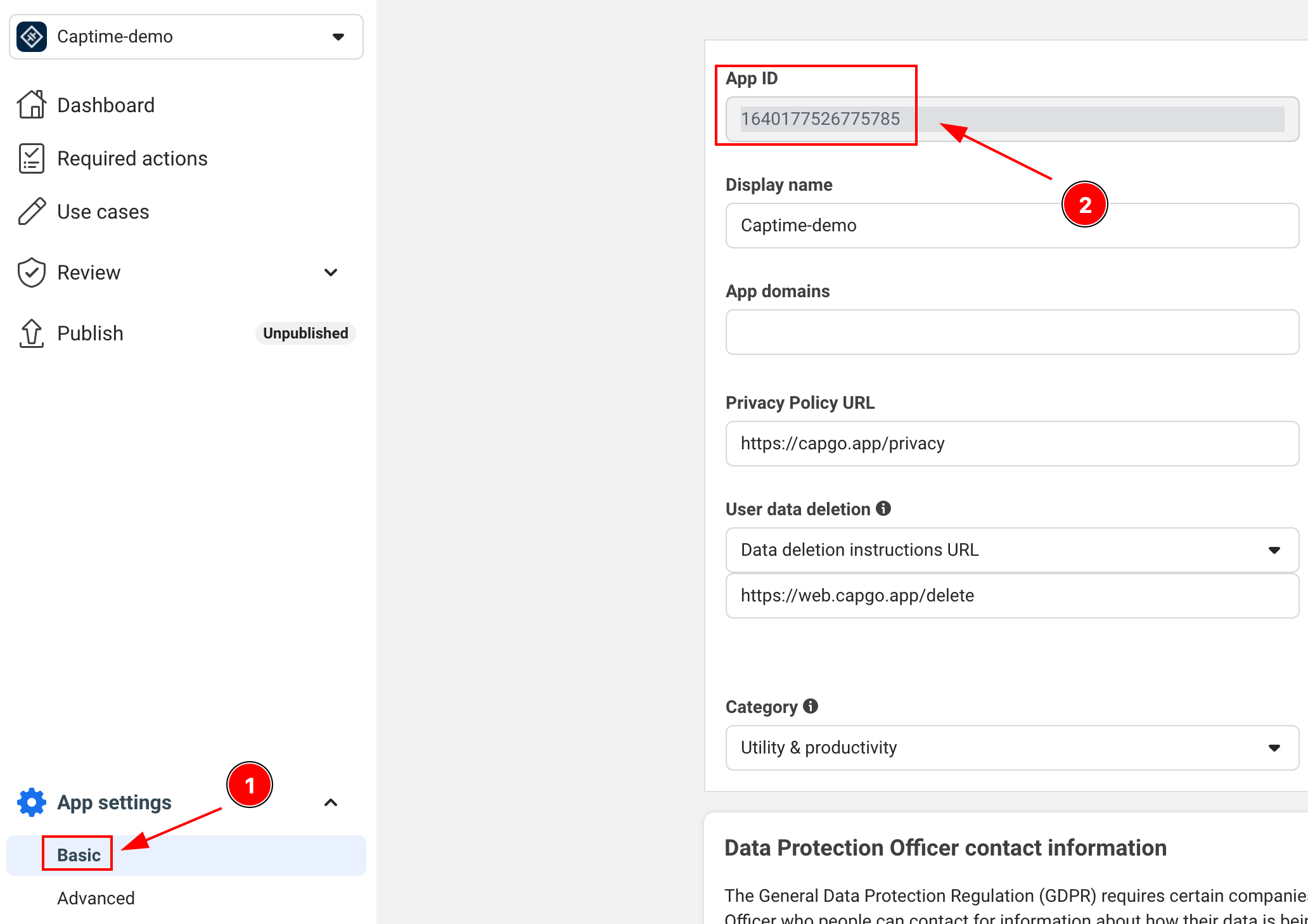
-
APP_NAME: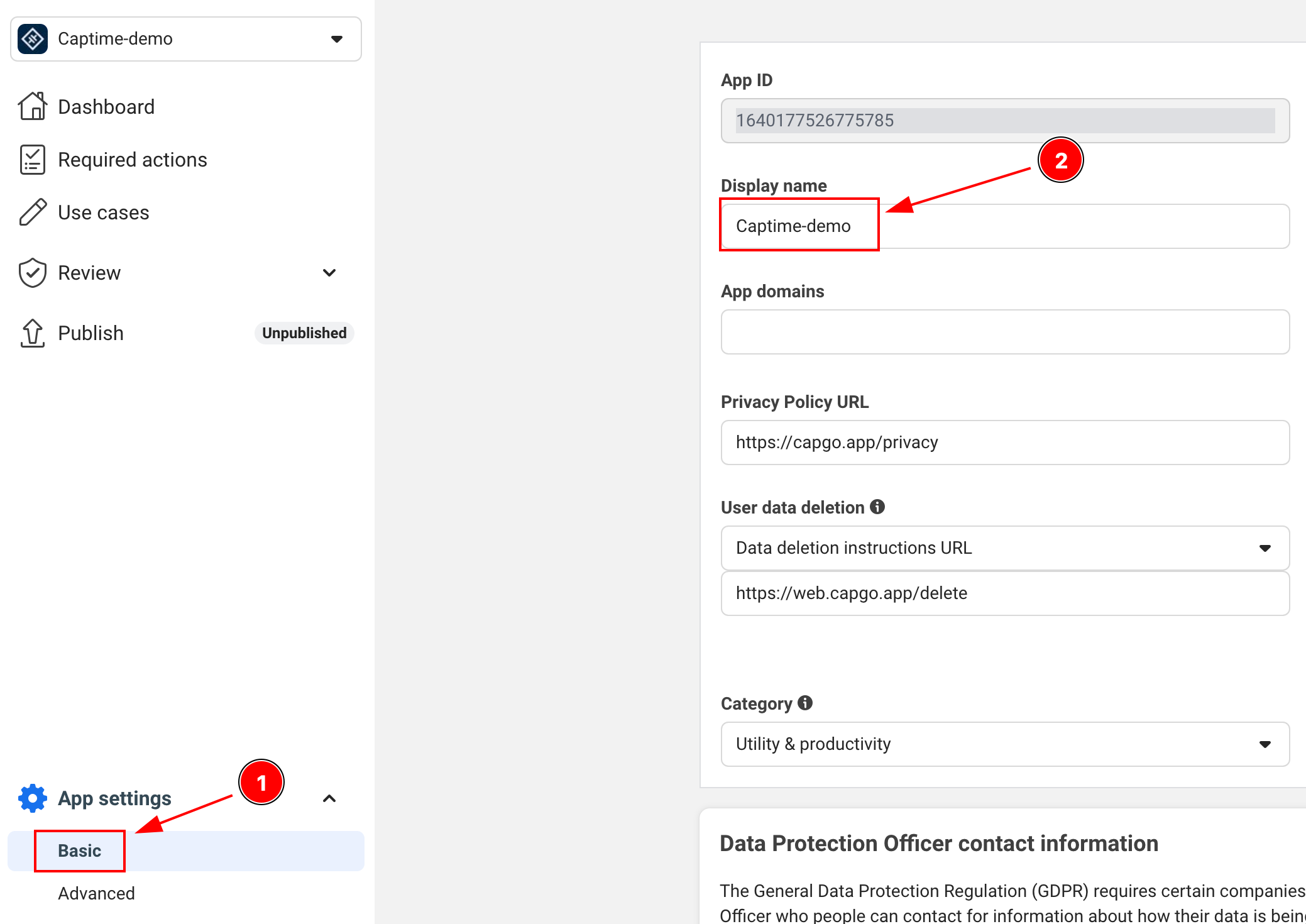
Androidの設定
Section titled “Androidの設定”-
AndroidManifest.xmlにインターネット権限を追加するこの行が存在することを確認してください:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/> -
Android key hashを生成する
これはFacebookが要求する重要なセキュリティ手順です。ターミナルを開いて次を実行します:
Terminal window keytool -exportcert -alias androiddebugkey -keystore ~/.android/debug.keystore | openssl sha1 -binary | openssl base64 -Aパスワードを求められたら、
androidを使用してください -
key hashをFacebookアプリに追加する
- Facebook Developersのアプリダッシュボードにアクセスします
- Settings > Basicに移動します
- 「Android」セクションまでスクロールします
- Androidがまだ追加されていない場合は「Add Platform」をクリックして詳細を入力します
- 生成したkey hashを追加します
- 本番環境では、デバッグとリリースの両方のkey hashを追加します
-
AndroidManifest.xmlを更新して次を含めます:<application>...<activity android:name="com.facebook.FacebookActivity"android:configChanges="keyboard|keyboardHidden|screenLayout|screenSize|orientation"android:label="@string/app_name" /><activityandroid:name="com.facebook.CustomTabActivity"android:exported="true"><intent-filter><action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /><category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /><category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" /><data android:scheme="FB[APP_ID]" /></intent-filter></activity></application>
iOSの設定
Section titled “iOSの設定”-
Facebook Developer ConsoleでiOSプラットフォームを追加する
- Facebook Developersのアプリダッシュボードにアクセスします
- Settings > Basicに移動します
- ページの一番下までスクロールして「Add Platform」をクリックします
- iOSを選択して必要な詳細を入力します
-
Xcodeプロジェクトを開き、Info.plistに移動します
-
Info.plistに次のエントリを追加します:
<key>FacebookAppID</key><string>[APP-ID]</string><key>FacebookClientToken</key><string>[CLIENT-TOKEN]</string><key>FacebookDisplayName</key><string>[APP-NAME]</string><key>LSApplicationQueriesSchemes</key><array><string>fbapi</string><string>fb-messenger-share-api</string></array><key>CFBundleURLTypes</key><array><dict><key>CFBundleURLSchemes</key><array><string>fb[APP-ID]</string></array></dict></array> -
AppDelegate.swiftを変更するimport FBSDKCoreKit@UIApplicationMainclass AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {// Override point for customization after application launch.// Initialize Facebook SDKFBSDKCoreKit.ApplicationDelegate.shared.application(application,didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: launchOptions)return true}func application(_ app: UIApplication, open url: URL, options: [UIApplication.OpenURLOptionsKey: Any] = [:]) -> Bool {// Called when the app was launched with a url. Feel free to add additional processing here,// but if you want the App API to support tracking app url opens, make sure to keep this callif (FBSDKCoreKit.ApplicationDelegate.shared.application(app,open: url,sourceApplication: options[UIApplication.OpenURLOptionsKey.sourceApplication] as? String,annotation: options[UIApplication.OpenURLOptionsKey.annotation])) {return true;} else {return ApplicationDelegateProxy.shared.application(app, open: url, options: options)}}}
アプリでFacebookログインを使用する
Section titled “アプリでFacebookログインを使用する”-
アプリでFacebookログインを初期化する
import { SocialLogin } from '@capgo/capacitor-social-login';// アプリ起動時に初期化await SocialLogin.initialize({facebook: {appId: 'APP_ID',clientToken: 'CLIENT_TOKEN',}}) -
ログイン関数を実装する
async function loginWithFacebook() {try {const result = await SocialLogin.login({provider: 'facebook',options: {permissions: ['email', 'public_profile'],limitedLogin: false // 重要な詳細については、以下のLimited Loginセクションを参照してください}});console.log('Facebook login result:', result);// ログイン成功を処理} catch (error) {console.error('Facebook login error:', error);// エラーを処理}} -
ユーザープロファイルデータを取得する
ログインが成功した後、追加のプロファイル情報を取得できます:
async function getFacebookProfile() {try {const profileResponse = await SocialLogin.providerSpecificCall({call: 'facebook#getProfile',options: {fields: ['id', 'name', 'email', 'first_name', 'last_name', 'picture']}});console.log('Facebook profile:', profileResponse.profile);return profileResponse.profile;} catch (error) {console.error('Failed to get Facebook profile:', error);return null;}}// ログイン後の使用例async function loginAndGetProfile() {const loginResult = await loginWithFacebook();if (loginResult) {const profile = await getFacebookProfile();if (profile) {console.log('User ID:', profile.id);console.log('Name:', profile.name);console.log('Email:', profile.email);console.log('Profile Picture:', profile.picture?.data?.url);}}}トークンタイプの制限:
getProfile呼び出しは、access token(トラッキングが許可されている標準ログイン)がある場合にのみ機能します。ユーザーがトラッキングを拒否した場合、またはlimited login(JWT tokenのみ)を使用している場合、この呼び出しは失敗します。その場合は、初回ログイン応答で提供されるプロファイルデータを使用してください。
⚠️ 重要: バックエンドトークン処理
Section titled “⚠️ 重要: バックエンドトークン処理”バックエンドは2つの異なるトークンタイプを処理する必要があります。iOSユーザーはApp Tracking Transparencyの選択に応じてaccess tokenまたはJWT tokenのいずれかを受け取る可能性があり、Androidユーザーは常にaccess tokenを受け取ります。
プラットフォーム別のトークンタイプ
Section titled “プラットフォーム別のトークンタイプ”| プラットフォーム | limitedLogin設定 | ユーザーATT選択 | 結果のトークンタイプ |
|---|---|---|---|
| iOS | true | 任意 | JWT Token |
| iOS | false | トラッキングを許可 | Access Token |
| iOS | false | トラッキングを拒否 | JWT Token(自動上書き) |
| Android | 任意 | N/A | Access Token(常に) |
バックエンド実装
Section titled “バックエンド実装”-
トークンタイプを検出して適切に処理する
async function loginWithFacebook() {try {const loginResult = await SocialLogin.login({provider: 'facebook',options: {permissions: ['email', 'public_profile'],limitedLogin: false // iOS: ATTに依存、Android: 無視される}});if (loginResult.accessToken) {// Access token(Androidは常に、iOSはトラッキングが許可されている場合)return handleAccessToken(loginResult.accessToken.token);} else if (loginResult.idToken) {// JWT token(iOSのみ、トラッキングが拒否された場合またはlimitedLogin: true)return handleJWTToken(loginResult.idToken);}} catch (error) {console.error('Facebook login error:', error);}} -
Firebase統合の例
import { OAuthProvider, FacebookAuthProvider, signInWithCredential } from 'firebase/auth';async function handleAccessToken(accessToken: string, nonce: string) {// Access tokenの場合は、OAuthProviderを使用(新しい方法)const fbOAuth = new OAuthProvider("facebook.com");const credential = fbOAuth.credential({idToken: accessToken,rawNonce: nonce});try {const userResponse = await signInWithCredential(auth, credential);return userResponse;} catch (error) {console.error('Firebase OAuth error:', error);return false;}}async function handleJWTToken(jwtToken: string) {// JWT tokenの場合は、バックエンドに送信して検証try {const response = await fetch('/api/auth/facebook-jwt', {method: 'POST',headers: {'Content-Type': 'application/json',},body: JSON.stringify({ jwtToken })});const result = await response.json();return result;} catch (error) {console.error('JWT validation error:', error);return false;}} -
バックエンドJWT検証
// バックエンド: FacebookからのJWT tokenを検証import jwt from 'jsonwebtoken';import { Request, Response } from 'express';app.post('/api/auth/facebook-jwt', async (req: Request, res: Response) => {const { jwtToken } = req.body;try {// Facebookの公開鍵でJWT tokenを検証// 参照: https://developers.facebook.com/docs/facebook-login/limited-login/token/validating/#standard-claimsconst decoded = jwt.verify(jwtToken, getFacebookPublicKey(), {algorithms: ['RS256'],audience: process.env.FACEBOOK_APP_ID,issuer: 'https://www.facebook.com' // From: https://www.facebook.com/.well-known/openid-configuration/?_rdr});// JWTからユーザー情報を抽出const userInfo = {id: decoded.sub,email: decoded.email,name: decoded.name,isJWTAuth: true};// アプリのセッション/トークンを作成const sessionToken = createUserSession(userInfo);res.json({success: true,token: sessionToken,user: userInfo});} catch (error) {console.error('JWT validation failed:', error);res.status(401).json({ success: false, error: 'Invalid token' });}}); -
汎用バックエンドトークンハンドラ
// バックエンドで両方のトークンタイプを処理async function authenticateFacebookUser(tokenData: any) {if (tokenData.accessToken) {// Access tokenを処理 - Facebook Graph APIで検証const response = await fetch(`https://graph.facebook.com/me?access_token=${tokenData.accessToken}&fields=id,name,email`);const userInfo = await response.json();return {user: userInfo,tokenType: 'access_token',expiresIn: tokenData.expiresIn || 3600};} else if (tokenData.jwtToken) {// JWT tokenを処理 - デコードして検証// 参照: https://developers.facebook.com/docs/facebook-login/limited-login/token/validating/#standard-claimsconst decoded = jwt.verify(tokenData.jwtToken, getFacebookPublicKey());return {user: {id: decoded.sub,name: decoded.name,email: decoded.email},tokenType: 'jwt',expiresIn: decoded.exp - Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000)};} else {throw new Error('No valid token provided');}}
主な考慮事項
Section titled “主な考慮事項”Access Token(標準ログイン):
- ✅ Android: 常に利用可能(iOS専用の制限は適用されません)
- ✅ iOS: ユーザーが明示的にアプリのトラッキングを許可した場合のみ
- ✅ Facebook Graph APIへのアクセスに使用可能
- ✅ より長い有効期限
- ✅ より多くのユーザーデータが利用可能
- ❌ iOSではあまり一般的でなくなっている、ユーザーがトラッキングを拒否することが増えているため
JWT Token(iOS専用プライバシーモード):
- ❌ Android: 発生しない(サポートされていない)
- ✅ iOS: トラッキングが拒否された場合、または
limitedLogin: trueの場合 - ✅ iOSユーザーのプライバシー設定を尊重
- ❌ 基本的なユーザー情報のみを含む
- ❌ より短い有効期限
- ❌ Facebook Graph APIへのアクセスなし
- ⚠️ 現在iOSユーザーで最も一般的なシナリオ
プラットフォーム固有の動作:
- iOSアプリ: access tokenとJWT tokenの両方を処理する必要があります
- Androidアプリ: access tokenのみを処理する必要があります
- クロスプラットフォームアプリ: 両方のトークン処理方法を実装する必要があります
セキュアコンテキストの要件(Web/Capacitor)
Section titled “セキュアコンテキストの要件(Web/Capacitor)”Crypto APIの制限
Section titled “Crypto APIの制限”更新されたFacebookログインフローには、nonceの生成にWeb Crypto APIが必要であり、これはセキュアコンテキストでのみ利用可能です:
// これはセキュアコンテキスト(HTTPSまたはlocalhost)が必要ですasync function sha256(message: string) { const msgBuffer = new TextEncoder().encode(message); const hashBuffer = await crypto.subtle.digest("SHA-256", msgBuffer); // ❌ セキュアでないコンテキストでは失敗します // ...}開発環境の問題
Section titled “開発環境の問題”よくある問題: HTTP URLのionic serveがFacebook認証を壊す
| 環境 | Crypto API利用可能 | Facebookログイン動作 |
|---|---|---|
http://localhost:3000 | ✅ はい | ✅ はい |
http://127.0.0.1:3000 | ✅ はい | ✅ はい |
http://192.168.1.100:3000 | ❌ いいえ | ❌ いいえ |
https://any-domain.com | ✅ はい | ✅ はい |
Capacitor開発のソリューション
Section titled “Capacitor開発のソリューション”-
Webテストにlocalhostを使用する
Terminal window # ionic serve --host=0.0.0.0の代わりにionic serve --host=localhost -
IonicでHTTPSを有効にする
Terminal window ionic serve --ssl -
実機でテストする
Terminal window # Capacitorアプリは実機上でセキュアコンテキストで実行されますionic cap run iosionic cap run android -
開発用の代替nonce生成
async function generateNonce() {if (typeof crypto !== 'undefined' && crypto.subtle) {// セキュアコンテキスト - crypto.subtleを使用return await sha256(Math.random().toString(36).substring(2, 10));} else {// 開発用のフォールバック(本番環境では安全ではありません)console.warn('Using fallback nonce - not secure for production');return btoa(Math.random().toString(36).substring(2, 10));}}
Firebase統合に関する注意
Section titled “Firebase統合に関する注意”最近のFirebaseドキュメントでは、ログイン設定に関係なく、Facebook認証にnonceを含むJWT tokenが必要です。このアプローチはlimitedLogin: trueとlimitedLogin: falseの両方で機能します:
// 両方のモードは、ユーザーの選択に応じてJWT tokenを返すことができます const loginResult = await SocialLogin.login({ provider: 'facebook', options: { permissions: ['email', 'public_profile'], limitedLogin: false, // true = 常にJWT、false = ユーザーのトラッキング選択に依存 nonce: nonce } });開発の制限: ネットワークIP(localhostではない)でionic serveを使用している場合、crypto APIの制限によりFacebookログインは失敗します。WebテストにはlocalhostまたはHTTPSを使用してください。
トラブルシューティング
Section titled “トラブルシューティング”よくある問題と解決策
Section titled “よくある問題と解決策”-
Androidのkey hashエラー
- Facebookダッシュボードに正しいkey hashを追加したことを再確認してください
- リリースビルドの場合は、デバッグとリリースの両方のkey hashを追加したことを確認してください
- hashを生成する際に正しいkeystoreを使用していることを確認してください
-
Facebookログインボタンが表示されない
- すべてのマニフェストエントリが正しいことを確認してください
- Facebook App IDとClient Tokenが正しいことを確認してください
- SDKを適切に初期化したことを確認してください
-
iOSのよくある問題
- すべてのInfo.plistエントリが正しいことを確認してください
- URL schemesが適切に設定されていることを確認してください
- bundle IDがFacebookダッシュボードに登録されているものと一致することを確認してください
-
テスト前に、Facebook Developer Consoleでテストユーザーを追加してください
- Roles > Test Usersに移動します
- テストユーザーを作成します
- これらの資格情報をテストに使用します
-
デバッグビルドとリリースビルドの両方をテストしてください
- デバッグkey hashを使用したデバッグビルド
- リリースkey hashを使用したリリースビルド
- エミュレータと実機の両方でテスト
次を含む完全なログインフローをテストすることを忘れないでください:
- ログイン成功
- ログインキャンセル
- エラー処理
- ログアウト機能
